Top 10 Tips for Choosing the Right Network Fiber Optic Cable for Your Needs
In today's digital landscape, the demand for high-speed data transmission has reached unprecedented levels, making the choice of the right network fiber optic cable more critical than ever. According to a report by the International Telecommunication Union (ITU), global internet traffic is projected to increase threefold from 2022 to 2025. This surge highlights the necessity for robust infrastructure capable of supporting bandwidth-hungry applications, such as cloud computing and video streaming. Network fiber optic cables, known for their superior speed and performance compared to traditional copper cables, are essential in meeting these growing demands.
Furthermore, the market for fiber optic cables is on a rapid upward trajectory, expected to reach $13.2 billion by 2027, as organizations increasingly adopt fiber optics for both commercial and residential applications. A comprehensive understanding of the various types of network fiber optic cables—including single-mode and multi-mode fibers—alongside their specifications, installation requirements, and compatibility with existing systems, ensures that businesses are equipped to make informed decisions. As we explore the top ten tips for choosing the right network fiber optic cable for your needs, it is crucial to navigate this evolving landscape with precise knowledge and strategic foresight.

Understanding Fiber Optic Cable Types and Their Applications
When selecting the right fiber optic cable, understanding the various types and their applications is crucial. Generally, fiber optic cables are categorized into two main types: single-mode and multi-mode. Single-mode fibers have a small core diameter and transmit data over longer distances with less signal loss, making them ideal for telecommunications and high-speed internet services. They are particularly effective in extensive networks where long-range data transmission is necessary.
On the other hand, multi-mode fibers feature a larger core, allowing multiple light modes to propagate simultaneously. This characteristic enables them to transmit data over shorter distances, making them well-suited for local area networks (LANs) and data centers where high bandwidth is critical over limited distances. Additionally, understanding the protective layers and environmental ratings of fiber optic cables can guide you in selecting the appropriate product for outdoor uses versus indoor installations, ensuring the longevity and performance of your network infrastructure.
Understanding Fiber Optic Cable Types and Their Applications
Evaluating Your Bandwidth and Speed Requirements
When selecting the right network fiber optic cable, one of the most critical factors to evaluate is your bandwidth and speed requirements. Understanding how much data you need to transmit at peak times will guide your decision. For instance, if your operations involve high-definition video conferencing or streaming large files, you will require cables that support higher speeds and can handle multiple data streams efficiently. On the other hand, if your network usage primarily consists of basic web browsing or email, a lower bandwidth capacity might suffice.
Tip: Always consider future expansion. As technology evolves, your bandwidth needs may increase, so it’s wise to choose a fiber optic cable that can accommodate potential upgrades. Look for cables that offer scalability, ensuring you won't need a complete overhaul if your demands grow.
Additionally, assess the distance between your devices. Fiber optic cables perform optimally over longer distances without signal degradation. If your setup requires extended stretches between connections, ensure you invest in cables that maintain high speeds over those distances.
Tip: Analyze your current usage patterns alongside your growth projections to make an informed choice about cable types and specifications. Planning ahead will save you from frequent upgrades and associated costs in the future.
Top 10 Tips for Choosing the Right Network Fiber Optic Cable for Your Needs
| Tip Number | Tip | Bandwidth Requirement | Cable Type | Ideal Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Determine your Internet speed needs | Up to 1 Gbps | Single-Mode | Residential Use |
| 2 | Consider future upgrades | 10 Gbps | Multi-Mode | Business Networks |
| 3 | Evaluate distance requirements | Up to 2 km | Single-Mode | Long Distance Connections |
| 4 | Check for installation environment | Variable | Indoor/Outdoor | Data Centers |
| 5 | Assess budget constraints | Up to 100 Gbps | Multi-Mode | Cost-Sensitive Projects |
| 6 | Factor in cable agility | Up to 400 Gbps | Flexible Multi-Mode | High-Performance Computing |
| 7 | Ensure compatibility with existing equipment | Up to 10 Gbps | LC/SC Connectors | Network Upgrades |
| 8 | Consult with professionals | Up to 100 Gbps | Custom Configurations | Specialized Applications |
| 9 | Examine warranties and support | N/A | Standard | All Use Cases |
| 10 | Research and compare options | Variable | Both Types | General Selection |
Assessing Cable Length and Installation Environment
When selecting the right network fiber optic cable, assessing the cable length and installation environment is crucial for optimal performance. According to the Fiber Optic Association, the maximum distance for single-mode fiber cables can reach up to 40 kilometers, while multimode fibers typically have a limit ranging from 300 to 400 meters, depending on the type of multimode installed. Therefore, understanding the distance your signal needs to travel is essential in determining the appropriate type of fiber optic cable to use, as exceeding these distances can lead to signal degradation and reduced speeds.
Additionally, the installation environment plays a significant role in cable selection. Factors such as temperature, susceptibility to interference, and exposure to moisture must be considered. For instance, cables installed outdoors may require additional ruggedness and protection against UV rays and extreme weather conditions. According to a report by the International Telecommunications Union, more than 20% of fiber optic failures are attributed to environmental factors. Therefore, selecting cables designed for specific environments, such as indoor-rated vs. outdoor-rated cables, ensures longevity and reliability of the network. Evaluating these aspects effectively can lead to improved network performance and reduced maintenance costs in the long run.
Choosing Between Single-Mode and Multi-Mode Fiber
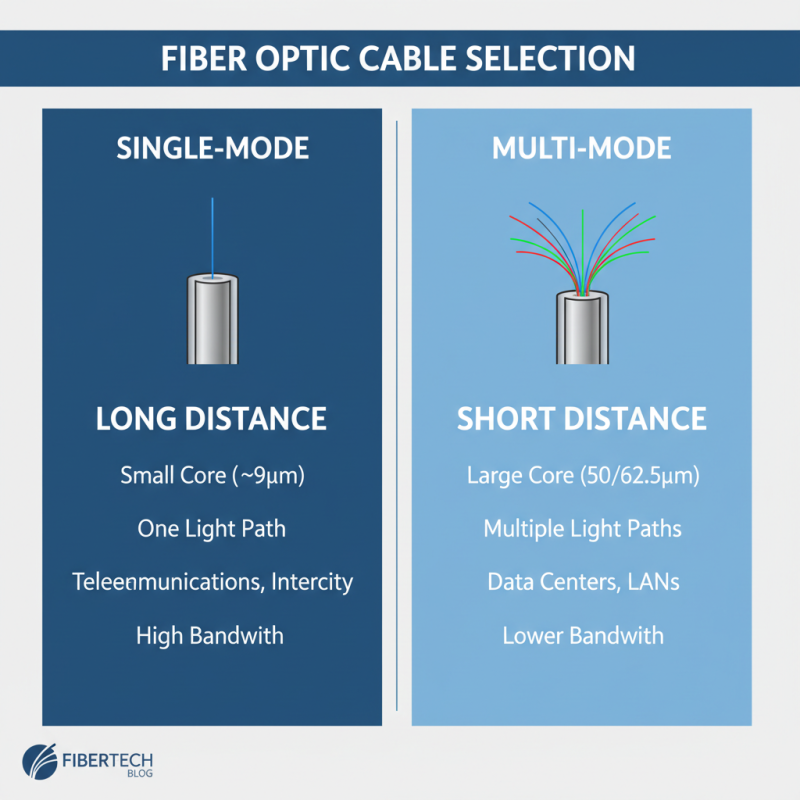
When selecting the right fiber optic cable for your network, one of the crucial decisions revolves around choosing between single-mode and multi-mode fibers. Single-mode fiber optics are designed with a small core diameter that allows only one light mode to pass through. This feature enables single-mode cables to transmit data over significantly longer distances, making them ideal for applications that require long-range communication, such as telecommunications and intercity network connections. Their ability to handle higher bandwidths also ensures that they can support high-speed internet and video streaming without significant signal degradation.
On the other hand, multi-mode fiber optics feature a larger core that allows multiple light modes to propagate simultaneously. This structure makes multi-mode fibers suitable for shorter distances, typically within buildings or across campuses. They are often more cost-effective for installations where high data rates are not needed over long distances. Additionally, multi-mode fibers can be easier to terminate and connect, which can simplify installation processes in environments where rapid deployment is essential. Understanding the distinctions between single-mode and multi-mode fibers will empower you to make an informed choice that aligns with your network's performance requirements and geographical challenges.
Comparing Cost Factors and Long-Term Value of Fiber Optic Cables
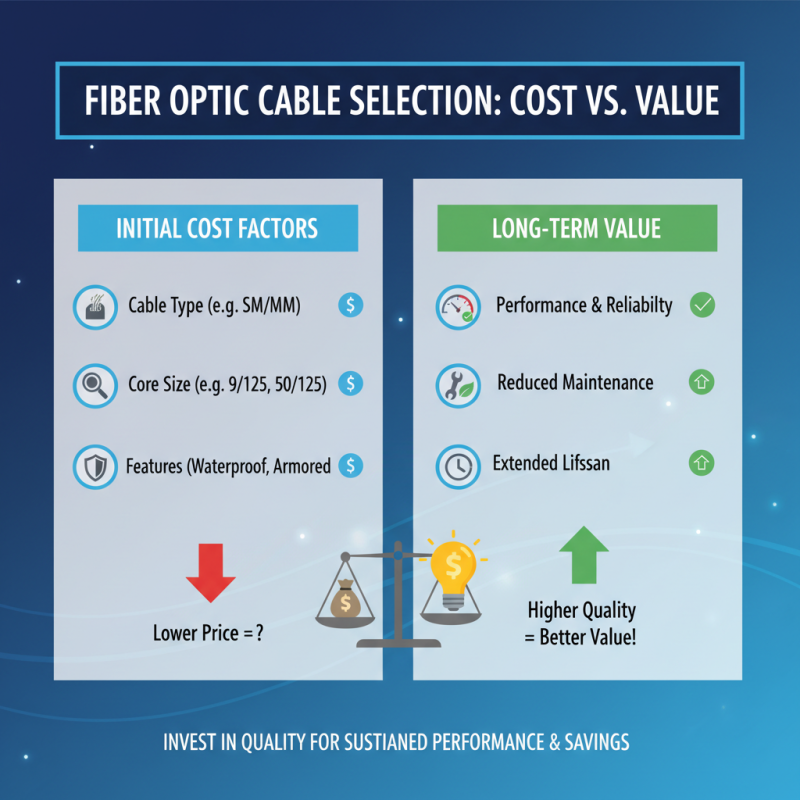
When selecting a fiber optic cable, understanding cost factors and long-term value is crucial. The initial purchase price of fiber optic cables can vary significantly based on specifications such as cable type, core size, and additional features like waterproofing or armoring. While it may be tempting to opt for the least expensive option, it is essential to consider the performance and reliability of the cable. In many cases, investing in higher-quality cables leads to reduced maintenance costs and fewer issues over the cable's lifespan, ultimately providing better value.
Additionally, evaluating the long-term value includes considering installation costs and future scalability. Some cables may require professional installation, which can increase upfront costs. However, the right choice can minimize additional expenses in the future, allowing for easier upgrades as needs evolve. Furthermore, examining manufacturer warranties and life expectancy ratings can help gauge how a particular cable will hold up over time, affecting both performance and the long-term financial investment. Striking the right balance between cost, quality, and long-term utility ensures that your fiber optic choice meets both immediate and future networking demands effectively.
Related Posts
-

What is the Importance of Network Fiber Optic Cable in Modern Communication
-

2025 Top Fiber Network Cable Innovations for Faster Connectivity Solutions
-

Exploring Market Trends for Cat 6a Patch Panels at the 138th Canton Fair in 2025
-

10 Reasons Why Cat 6 Bulk Cable is Essential for Your Network Installation
-

What is Networking Infrastructure and Why it Matters for Your Business
-

Understanding the Impact of Cat 6A Cables on Network Performance and Future-Proofing Your Business
