Top 10 Patch Cable Tips to Enhance Your Network Performance and Connectivity
In today’s fast-paced digital landscape, ensuring optimal network performance is crucial for both individuals and businesses.
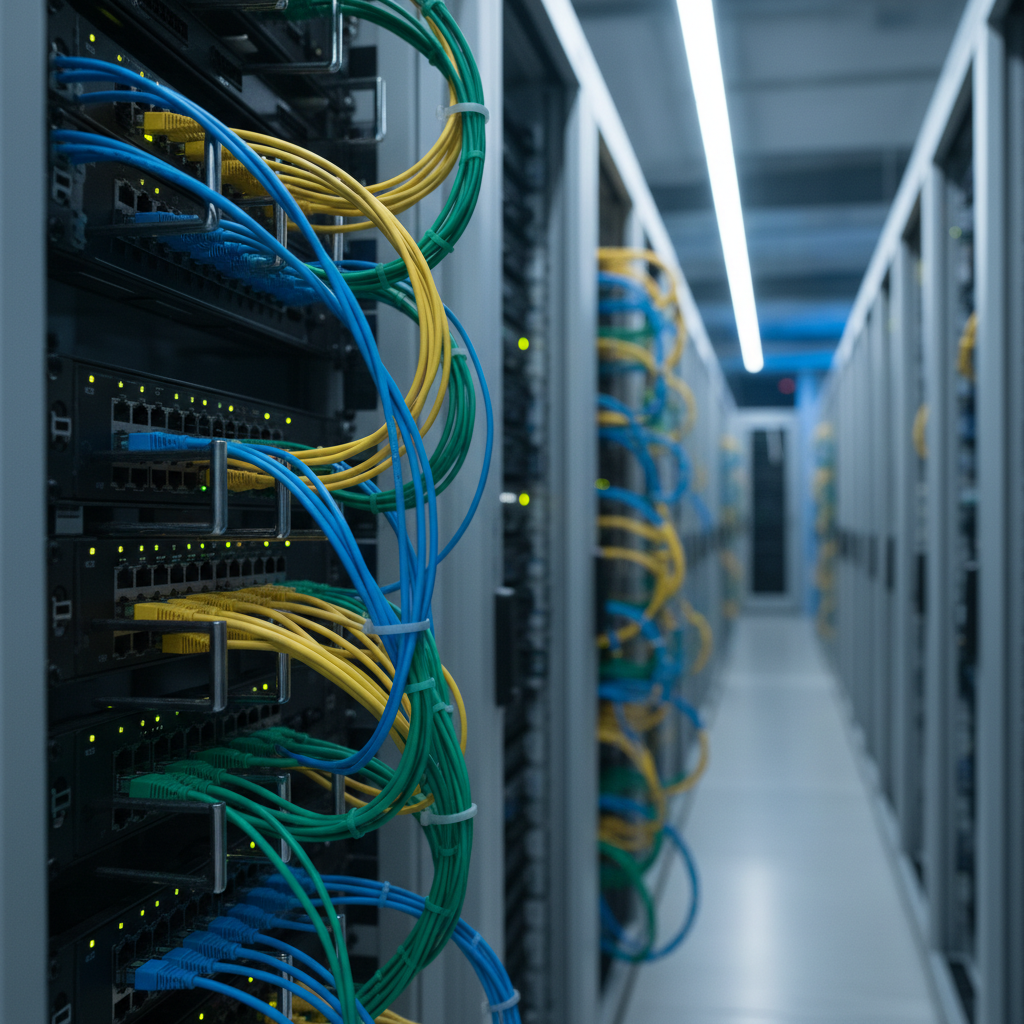 Patch cables play a vital role in connecting network devices, and understanding their usage can significantly enhance connectivity.
As John Doe, a leading expert in the networking industry, aptly states, “The quality and organization of your patch cables can make all the difference in the speed and reliability of your network.”
Patch cables play a vital role in connecting network devices, and understanding their usage can significantly enhance connectivity.
As John Doe, a leading expert in the networking industry, aptly states, “The quality and organization of your patch cables can make all the difference in the speed and reliability of your network.”
With numerous options available, selecting the right patch cable can be overwhelming, but being informed about the best practices can lead to a more efficient network environment.
From cable length to material, there are several factors to consider that impact performance.
By exploring the top ten patch cable tips, users can fine-tune their network setup, minimize potential issues, and achieve seamless connectivity at home or in the workplace.
This guide aims to shed light on essential considerations that can maximize the effectiveness of patch cables, helping you navigate through the complexities of networking and ultimately improving the overall performance of your network.
Understanding the Importance of High-Quality Patch Cables in Network Efficiency
High-quality patch cables play a crucial role in maximizing the efficiency of any network. They are the unsung heroes that ensure seamless connectivity between devices, minimizing signal loss and interference. When choosing patch cables, look for those with robust shielding and connectors that offer reliable performance. This is essential in maintaining data integrity, especially in environments with heavy network traffic.
One important tip for enhancing network performance is to avoid excessively long cables. Longer cables can introduce latency and attenuation that can compromise signal quality. Instead, opt for the shortest length necessary to connect your devices. Additionally, always keep cables organized and free from tangles to prevent physical strain on the connectors, which can lead to wear over time.
Another consideration is the category of the cable. For instance, using category 6 or above can significantly boost your network's speed and efficiency, particularly in high-bandwidth applications. Investing in high-quality patch cables tailored to your specific network needs can lead to improved performance and connectivity, ensuring that you get the most out of your infrastructure.
Top 10 Patch Cable Tips to Enhance Your Network Performance and Connectivity
| Tip No. | Tip Description | Benefits | Recommended Length |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Use Cat6 or higher cables | Increased speed and reduced interference | Up to 100 meters |
| 2 | Keep cable length to a minimum | Reduced latency and signal loss | Less than 30 meters for best performance |
| 3 | Avoid sharp bends in cables | Prevents damage to cabling and maintains performance | N/A |
| 4 | Use stranded cables for patching | More flexible and ideal for patch panels | N/A |
| 5 | Test cables before use | Ensures functionality and quality | N/A |
| 6 | Label cables clearly | Easier troubleshooting and management | N/A |
| 7 | Use cable ties wisely | Prevents tangling while avoiding stress on cables | N/A |
| 8 | Avoid running cables near power lines | Reduces electromagnetic interference | N/A |
| 9 | Maintain proper humidity and temperature | Prolongs cable lifespan and performance | N/A |
| 10 | Regularly inspect cables | Identifies wear and tear early | N/A |
Identifying the Right Cable Length: How Distance Affects Signal Integrity and Latency
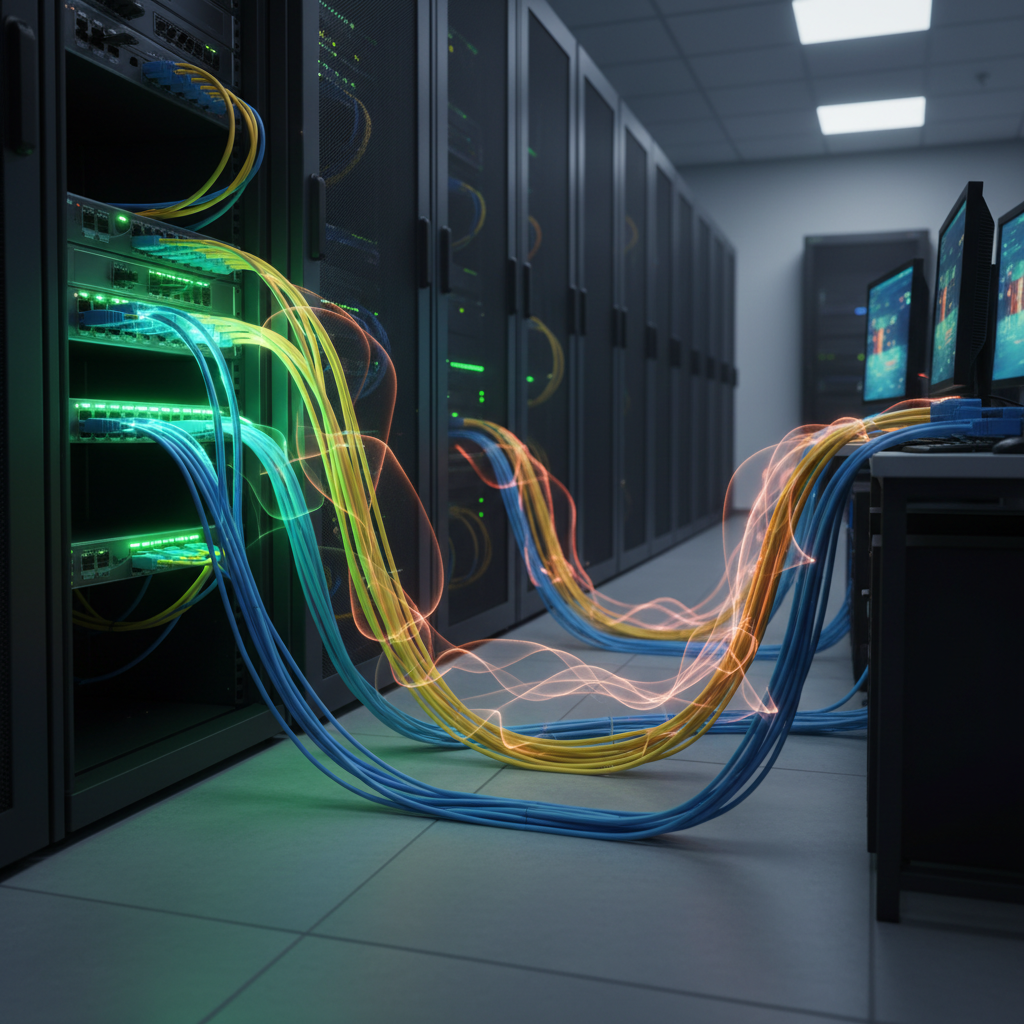

When it comes to optimizing network performance, selecting the right patch cable length is crucial.
Distance can significantly impact signal integrity and latency, particularly in high-speed environments. According to industry research, a signal can degrade as the distance between the source and destination increases, often leading to increased latency and packet loss.
For instance, Ethernet standards indicate that the maximum cable length should not exceed 100 meters for Cat5e and Cat6 cables to maintain optimal performance.
To ensure efficient connectivity, consider these tips: First, measure the distance between your devices accurately and add a little extra length to accommodate cable routing.
This prevents tension and maintains signal quality. Second, keep in mind that longer cables may require higher quality materials to minimize attenuation.
For example, using a shielded twisted pair (STP) cable instead of an unshielded twisted pair (UTP) can enhance performance in environments with significant electromagnetic interference.
Lastly, regularly test your cables with a cable tester to ensure they meet performance standards; this can help identify potential issues before they escalate.
Implementing these tips while considering cable length will help maintain the integrity of your network connections, ultimately leading to better efficiency and performance in data transmission.
Best Practices for Cable Management: Reducing Interference and Improving Airflow in Rack Systems
Effective cable management is essential for optimizing network performance and ensuring reliable connectivity. According to a report by the Telecommunications Industry Association (TIA), up to 50% of network issues can be traced back to poor cabling practices. When organization and routing of cables are neglected, it can lead to increased electromagnetic interference (EMI), which negatively impacts data transmission speeds and overall network efficiency. By employing structured cabling systems and clearly labeling each cable, network professionals can significantly reduce confusion and enhance troubleshooting efforts.
Moreover, proper cable spacing is crucial for maintaining airflow within rack systems. The American National Standards Institute (ANSI) emphasizes that insufficient airflow can lead to overheating, which can cause significant hardware failure and downtime. Solutions like vertical and horizontal cable management solutions should be utilized to ensure that cables do not obstruct airflow paths. By implementing these best practices, networks can operate at optimal performance levels, reducing heat buildup and enhancing the longevity of network equipment.
Top 10 Patch Cable Tips to Enhance Your Network Performance
Choosing Between Shielded and Unshielded Cables: Key Factors for Optimal Performance
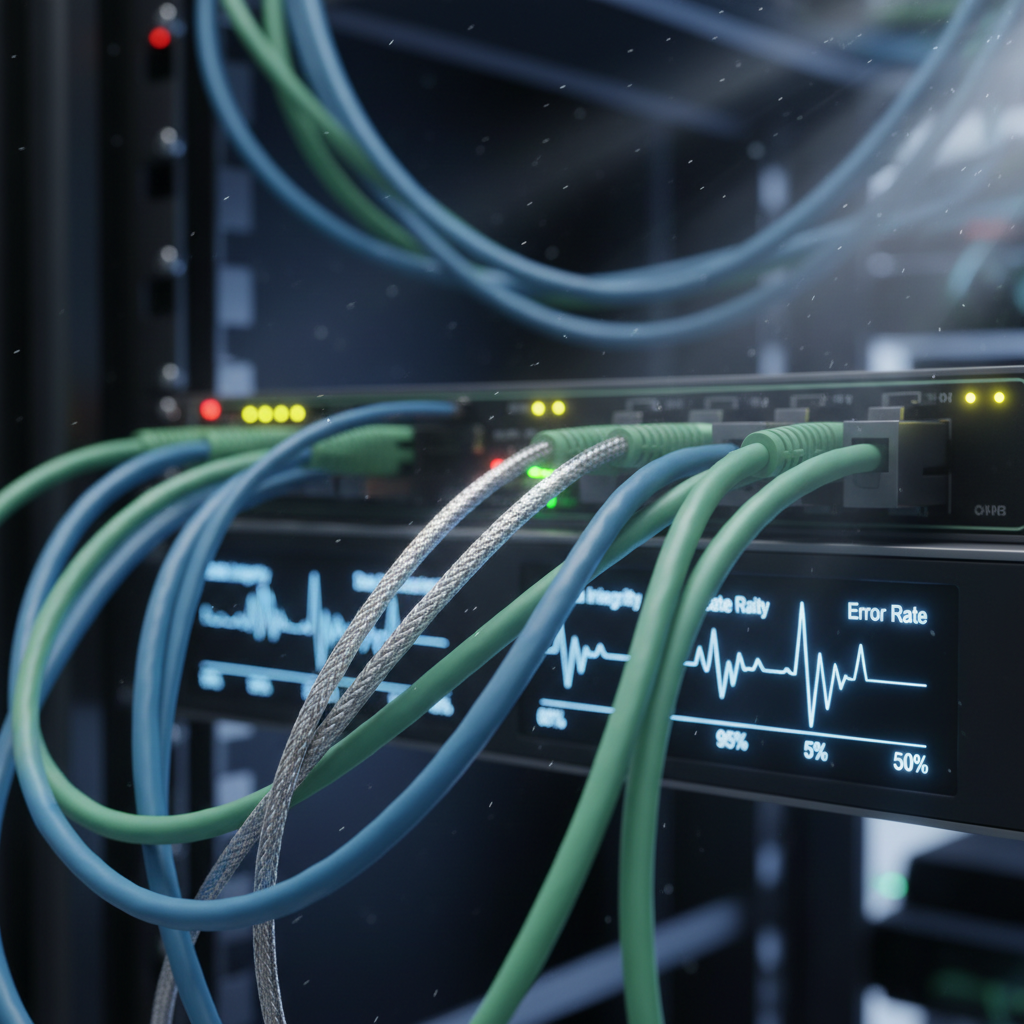

When selecting the appropriate patch cables for your network, choosing between shielded and unshielded cables is crucial to achieving optimal performance.
Shielded cables, equipped with a protective layer that reduces electromagnetic interference (EMI), are particularly beneficial in environments rife with potential disruptions, such as data centers or industrial locations.
According to a report by the Telecommunications Industry Association (TIA), the use of shielded cables can improve data integrity and reduce error rates by up to 30%, making them a worthwhile investment for high-demand applications.
On the other hand, unshielded cables are often sufficient for less congested environments, such as standard office spaces. These cables are generally more affordable and easier to install, which may appeal to businesses with lower data transmission demands. However, it's important to note that unshielded cables can struggle in areas with high interference, resulting in decreased performance.
Research indicates that unshielded twisted pair (UTP) cables can experience performance drops of around 20% in environments with significant EMI. Ultimately, the choice between shielded and unshielded cables should be guided by the specific needs of your network environment, balancing performance requirements with budgetary constraints.
Regular Maintenance and Testing of Patch Cables: Prolonging Lifespan and Ensuring Reliability
Regular maintenance and testing of patch cables are essential for extending their lifespan and ensuring reliability within any network infrastructure. Much like the long-lasting photovoltaic components, which have a design lifespan of 25-30 years, patch cables can also achieve prolonged durability with proper care. Periodically checking for wear and tear, ensuring secure connections, and eliminating potential sources of interference can significantly enhance the performance of your network.
Moreover, just as regular inspections are vital in maintaining fire safety equipment in buildings, routine testing of patch cables is crucial in preventing network downtime. Employing tools to test signal integrity and identifying faulty cables before issues arise can enhance overall connectivity. In doing so, organizations can conserve resources and maintain a robust network, akin to the well-maintained railway machinery which contributes to efficient transportation systems. Prioritizing these maintenance practices not only fosters reliability but also supports the smooth operation of essential network services.
Related Posts
-

7 Best Patch Cable Options for Seamless Connectivity Solutions in 2023
-

Ultimate Guide to Choosing the Right Network Patch Cable for Your Home Setup
-

Top 5 Networking Certification Programs to Boost Your Career Today
-

Innovative Solutions for Optimizing Enterprise Networking Efficiency
-

How to Choose the Right Patch Panel for Your Networking Needs
-
Unlocking the Power of LC Patch Panels: A Comprehensive Guide for Network Optimization
